关于地球
地球,是太阳系八大行星之一,是距离太阳第三近的行星,约1.5亿公里,46亿年以前起源于原始太阳星云。地球表面71%为海洋,29%为陆地,是目前宇宙中已知的唯一有生命存在的天体,是包括人类在内上百万种生物赖以生存的绿色家园。大约在46亿年前,从太阳系的星云中分化成原始地球,形成时一片荒芜,经过了几十亿年的演化,逐渐形成了生机盎然的地球。
About the Earth
The earth, as one of the eight planets of the solar system, is the third planet away from the Sun --- about 150 million km, and is originated from the original solar nebula about 4.6 billion years ago. 71% of the earth's surface is covered by ocean and 29% by land. The earth is the only known celestial body with lives in the cosmos and is also the green home that millions of creatures including human rely for existence.About 4.6 billion years ago, disintegrated from the nebula of solar system, the earth had a barren landscape, but with billions of evolution, the earth becomes exuberan
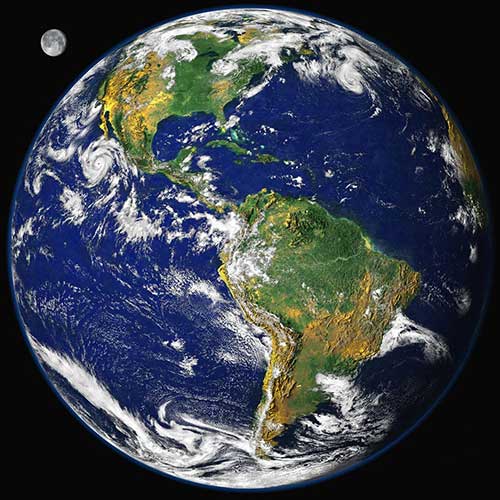

地球 Earth
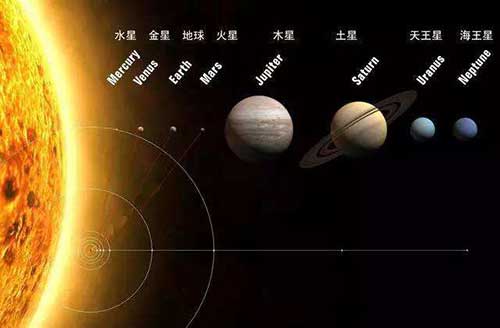
太阳系 The Solar System
地球的起源和演化
大约在46亿年前,从太阳系的星云中分化成原始地球,形成时一片荒芜,经过了十几亿年的演化,逐渐形成了生机盎然的地球。
The Origin and Evolution of the Earth
About 4.6 billion years ago, disintegrated form the nebula of the solar system, the earth had a barren landscape, but with billions of years of evolution, the earth becomes exuberant.
冥古宙(38亿 年前)地球景观
Earth Landscape during Hadean(3.8 billion years ago)
早期地球复原图--岩浆冷凝及海洋起源
Reconstruction Figure of the early Earth--Magma cooling and Marine Origin
地球表面演化:大陆漂移
The Evolution of the Earth Surface: Continental Drift
地球的圈层结构
地球圈层结构分为地球外部圈层和地球内部圈层两大部分。外部圈层可分为大气圈、水圈、生物圈等;内部圈层可分为地壳、地幔和地核三个主要的圈层。
The Layered Structure of the Earth
The earth can be divided into outer circle layer and inner circle layer. The outer circle is divided into atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere and so on; the inner circle is divided into three main layers including crust, mantle and core.
大地之书
地球上最古老的地层距今已有39亿年了,在漫长的地质历史长河中,不同时间段形成的岩层相互叠层,就如同一本书的书页一样,面对如此厚重的“大地之书”,我们该如何探索其中的奥秘呢?地质学家们按地层形成的时代来划分出“章节“, 就像历史学家把我国的历史划分为唐、宋、元、明、清那样,每一个年代所形成的地层,就按这个年代名来命名。宙、代、纪、世、期代表地质年代,与其对应的地层单位就是宇、界、系、统、阶。
The Book of Earth
The oldest stratum on the earth formed 3.9 billion years ago. In the long geological history, rock strata forming in different time are mutually laminated, like the pages of a book. When we face such heavy “The Book of Earth”, how could we explore the mystery? The geologists divided the strata into “chapters” based on formation era of the strata, like the division of the history of our country into Tang, Song, Yuan, Ming, Qing dynasties made by the historians. Each stratum that formed in different eras is named after the formation era. “Eon”, “Era”, “Period”, “Epoch” and “Age” present geological time scales, the corresponding stratigraphic unit is "eonothem", "erathem", "system", "series", and "stage" respectively.
生命的演化
地球上生命的演化是一个非常漫长的过程。在地球形成后的30多亿年左右,出现了最原始的单细胞生物,随着时间的推移,从简单到复杂、从低等到高等、从单细胞到多细胞,生物越来越复杂多样。大约在2百万年前,人类出现,代表了地球生物演化的最高阶段。
The Evolution of Life
It takes an extremely long period of time for the evolution of life. The primitive unicellular organism appeared about 3 billion years after the earth was formed. As time goes on, creatures are becoming more and more complicated — from simplicity to complex, inferiority to superiority, unicellular organism to multicellular organism. About 2 million years ago, the appearance of human beings is the symbol of the highest stage of biological evolution on Earth.
探寻岩石的奥秘
岩石俗称石头,是天然产出的由一种或多种矿物或其它物质构成的固态集合体,它构成地球的岩石圈(地壳和上地幔)。按照岩石形成过程的不同,可划分为火成岩(也称岩浆岩)、沉积岩、变质岩三大类。
Explore the Mystery of Rocks
Rock, commonly know as the stone, is a naturally produced solid-state aggregation which consists of one or more minerals or other materials. They constitute the lithosphere (crust and upper mantle) of the earth. According to different formation processes of rocks, they can be divided into three rock types including igneous rocks (also known as magmatic rocks), sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks.
火成岩:也称岩浆岩,是由来自地球深部炽热的岩浆固结而成的岩石。岩浆岩按产状可分为侵入岩(岩浆侵入到地壳一定深度内,缓慢冷凝固结形成侵入岩)和喷出岩(岩浆喷出地表,沿坡流动,迅速冷凝固结形成喷出岩)。
Igneous rock: Igneous rocks, also called magmatic rocks, are kind of rocks formed by solidification of hot magma derived from the deep earth. According to their occurrence, magmatic rocks can be divided into intrusive rocks (magma intrudes the crust within certain depth with slow condensation and consolidation forming intrusive rocks) and extrusive rocks (magma erupts above the surface and flows along the slope with rapid condensation and consolidation forming extrusive rocks).
岩浆岩 Magmatic Rock
沉积岩:是在地表条件下,母岩经风化作用、生物作用、化学作用和某种火山作用的产物,经过搬运、沉积,并经胶结、压实和重结晶形成的层状岩石。
Sedimentary rock: Sedimentary rocks are formed under the condition of the earth's surface. They are produced by transportation and deposition after parent rocks undergoing weathering, biological effect, chemical action and kind of volcanism forming layered rocks through cementation, compaction and recrystallization.
沉积岩 Sedimentary Rock
变质岩:先期形成的火成岩、沉积岩或变质岩,经变质作用(如温度、压力等物理条件的巨大变化或具有化学活动性流体的强烈影响),变成具有新的矿物组合及变质结构与构造特征的岩石。
Metamorphic rock: Previously formed igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks or metamorphic rocks, which underwent metamorphism (such as great changes of temperature, pressure and other physical conditions; or strong influence of chemically active fluid), would form a type of rocks that has new mineral assemblages with characteristics of metamorphic textures and structures.
随着温度和压力的增加,变质程度逐渐加深,岩石矿物成分和结构特征与原岩差别越来越大。
With temperature and pressure increasing, metamorphism grade would be gradually increased and mineral compositions and structure characteristics of rocks would have a bigger and bigger difference from the original rocks.
常见变质岩类型 Common Types of Metamorphic Rocks
With Temperature and Pressure metamorphic rocks's Change
3大类岩石的形成与转化
岩浆岩、沉积岩、变质岩这三种岩石在一定的条件下是可以相互转化的。
Formation and Transfomation of Three Kinds of Rocks
Magmatic rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks can be transformed into each other under certain circumstances
绚丽多彩的矿物
矿物是由地质作用所形成的天然单质或化合物。它们具有相对确定的化学组成,而且大多数具有一定的晶体形态,是组成岩石的基本单元,目前已知的矿物约有4145种。
The Colorful Mineral
Minerals are natural elementary substance or compound formed by geological processes. They have relatively definite chemical composition and most have a certain crystal form. They are the basic unit forming rocks.About 4145 kinds of minerals have been known so far.
常见等轴晶系矿物晶体形态 The Common Shape of Cubic System Mineral Crystal
矿物分类 Classification of Minerals
矿物的分类
按照物质成分的不同,矿物可划分成以下5大类:自然元素矿物、硫化物及其类似化合物矿物、氧化物和氢氧化物矿物、含氧盐矿物(碳酸盐,硝酸盐和硼酸盐矿物、硫酸盐和铬酸盐、磷酸盐、砷酸盐、钒酸盐、钼酸盐和钨酸盐、有机矿物、硅酸盐矿物)和卤化物矿物。
Classification of minerals
Based on different material compositions, minerals can be divided into the following five categories, including natural element mineral, sulfide mineral and its similar compound mineral , oxide and hydroxide, oxysalt mineral(including carbonate, nitrate and borate mineral, sulfate and chromate, phosphate, arsenate, vanadate, molybdate and tungstate, organic mineral, silicate mineral) and halide mineral .
什么是化石?
化石是经过自然作用,保存于地层中的古生物遗体、遗迹以及生物成因的残余有机分子,通俗地说,化石就是生活在遥远过去生物的遗体或遗迹变成的石头。
What Is a Fossil
Fossil is defined as representing both palaeobios remains/traces and residual organic molecules of biological origin, which are preserved in stratum by natural role. In layman's terms, fossil is kind of a stone become from bodys or traces of living beings in the distant past.
化石的分类 Classification of Fossil
化石的主要用途 The Main use of Fossils
按照保存形式,化石可分为实体化石、模铸化石、遗迹化石和化学化石4类。
According to the preservation way, fossil can be divided into four categories including body fossil, cast fossil,trace fossil and chemical fossil.
1、实体化石:生物的遗体或遗体的模铸保留下来形成的化石。
Body fossil: represented by almost all or part of paleobios remains preserved nowadays.
2、模铸化石:古生物的遗体留在地层中的痕迹或复铸物。
Cast fossil: traces or compound casting materials that paleobios remains reserve in stratum.
3、遗迹化石:古生物保留在地层中的活动痕迹或遗物,形成的化石。
Trace fossil: a fossil formed by a trace or mark left behind by an organism.
4、化学化石:组成生物体的残留有机物分子,在岩石中保存下来,形成化石。
Chemical fossil: a fossil represented by the chemical remains of an organism preserved in the rocks.